FAQ
Frequently Asked Question
PMBOK GUIDE 6th Edition:
Chapter 10 PROJECT COMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT
Chapter 13 Project Stakeholder Management
Pertanyaan (silahkan dijawab dan masing2nya merujuk ke halaman berapa di PMBOK):
1. Apa Objective dari Project Communications Management?
Apa tujuan dari Plan Communications Management?
Apa tujuan dari Manage Communications? Apa tujuan dari Monitor Communications?
Project Communications Management includes the processes necessary to ensure that the information needs of the project and its stakeholders are met through the development of artifacts and the implementation of activities designed to achieve effective information exchange.
Plan Communication Management is the process of developing an appropriate approach and plan for project communication activities based on the information needs of each stakeholder or group, available organizational assets, and the needs of the project.
Manage Communication is The process of ensuring timely and appropriate collection, creation, distribution, storage, retrieval, management, monitoring, and the ultimate disposition of project information
Monitor Communication is The process of ensuring the information needs of the project and its stakeholders are met.
page 359
2. Jelaskan dengan contoh, dimensi-dimensi dalam aktivitas komunikasi.
Communication activities have many dimensions, including but not limited to:
- Internal. Focus on stakeholders within the project and within the organization.
- External. Focus on external stakeholders such as customers, vendors, other projects, organizations, government, the public, and environmental advocates.
- Formal. Reports, formal meetings (both regular and ad hoc), meeting agendas and minutes, stakeholder briefings, and presentations.
- Informal. General communications activities using emails, social media, websites, and informal ad hoc discussions.
- Hierarchical focus. The position of the stakeholder or group with respect to the project team will affect the format and content of the message, in the following ways:
- Upward. Senior management stakeholders.
- Downward. The team and others who will contribute to the work of the project.
- Horizontal. Peers of the project manager or team.
- Official. Annual reports; reports to regulators or government bodies.
- Unofficial. Communications that focus on establishing and maintaining the profile and recognition of the project and building strong relationships between the project team and its stakeholders using flexible and often informal means.
- Written and oral. Verbal (words and voice inflections) and nonverbal (body language and actions), social media and websites, media releases.
page 361
3. Jelaskan pengertian 5C’s of written communications.
Mengapa 5C’s perlu didukung oleh ketrampilan berkomunikasi?
- Correct grammar and spelling. Poor use of grammar or inaccurate spelling can be distracting and can also introduce distortions in the message, diminishing credibility.
- Concise expression and elimination of excess words. A concise, well-crafted message reduces the opportunities for misunderstanding the intent of the message.
- Clear purpose and expression directed to the needs of the reader. Ensure that the needs and interests of the audience are factored into the message.
- Coherent logical flow of ideas. A coherent logical flow of ideas and using “markers” such as introduction and summaries of the ideas throughout the writing.
- Controlling flow of words and ideas. Controlling the flow of words and ideas may involve graphics or just summaries.
4. Faktor-faktor apakah yang mempengaruhi pemilihan communication technology?
Factors that can affect the choice of communication technology include: - Urgency of the need for information. The urgency, frequency, and format of the information to be communicated may vary from project to project and also within different phases of a project. - Availability and reliability of technology. The technology that is required for distribution of project communications artifacts should be compatible, available, and accessible for all stakeholders throughout the project. - Ease of use. The choice of communication technologies should be suitable for project participants and proper training events should be planned, where appropriate. - Project environment. Whether the team will meet and operate on a face-to-face basis or in a virtual environment; whether they will be located in one or multiple time zones; whether they will use multiple languages for communication; and finally, whether there are any other project environmental factors, such as various aspects of culture, which may constrain the efficiency of the communication. - Sensitivity and confidentiality of the information. Some aspects to consider are: -Whether information to be communicated is sensitive or confidential. If so, additional security measures may be required. - Social media policies for employees to ensure appropriate behavior, security, and the protection of proprietary information.
page. 370.
Apa saja beda penggunaan Communication technology pada Plan Communications Management dan Manage Communications?
The methods used to transfer information among project stakeholders may vary significantly. Common methods
used for information exchange and collaboration include conversations, meetings, written documents, databases, social
media, and websites.
IN manage communication : The choice of communication methods should allow flexibility in the event that the membership of the stakeholder community changes or their needs and expectations change.COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
Described in Section 10.1.2.3. Factors that influence the technology include whether the team is colocated, the
confidentiality of any information that needs to be shared, resources available to the team members, and how the
organization’s culture influences the way in which meetings and discussions are normally conducted.
5. Jelaskan tentang communication methods. Apa bedanya penggunaan Communication methods pada Plan Communications Management dan Manage Communications?
There are several communication methods that are used to share information among project stakeholders. These methods are broadly classified as follows: - Interactive communication. Between two or more parties performing a multidirectional exchange of information in real time. It employs communications artifacts such as meetings, phone calls, instant messaging, some forms of social media, and videoconferencing. - Push communication. Sent or distributed directly to specific recipients who need to receive the information. This ensures that the information is distributed but does not ensure that it actually reached or was understood by the intended audience. Push communications artifacts include letters, memos, reports, emails, faxes, voice mails, blogs, and press releases. - Pull communication. Used for large complex information sets, or for large audiences, and requires the recipients to access content at their own discretion subject to security procedures. These methods include web portals, intranet sites, e-learning, lessons learned databases, or knowledge repositories.
page 374
Communication method pada:
1. Plan
Interactive, Push dan Pull
2. Manage
The choice of communication methods should allow flexibility in the event that the membership of the stakeholder community changes or their needs and expectations change.
page. 383
6. Jelaskan tentang communication models. Sebutkan elemen apa yang penting untuk diperhatikan dalam communication models yang menentukan langkah-langkah komunikasi basic dan interaktif. Jelaskan juga langkah-langkah tersebut. Apa tanggung jawab sender dan receiver dalam proses komunikasi?
Definition: A description, analogy, or schematic is used to represent how the communication process will be performed for the project.
Communication models can represent the communication process in its most basic linear form (sender and receiver), in a more interactive form that encompasses the additional element of feedback (sender, receiver, and feedback), or in a more complex model that incorporates the human elements of the sender(s) or receiver(s) and attempts to show the complexity of any communication that involves people. - Sample basic sender/receiver communication model. This model describes communication as a process and consists of two parties, defined as the sender and receiver. This model is concerned with ensuring that the message is delivered, rather than understood. The sequence of steps in a basic communication model is: - Encode. The message is coded into symbols, such as text, sound or some other medium for transmission (sending). - Transmit message. The message is sent via a communication channel. The transmission of this message may be compromised by various physical factors such as unfamiliar technology or inadequate infrastructure. Noise and other factors may be present and contribute to loss of information in transmission and/or reception of the message. - Decode. The data received is translated by the receiver back into a form useful to the receiver. - Sample interactive communication model. This model also describes communication as a process consisting of two parties, the sender and receiver, but recognizes the need to ensure that the message has been understood. In this model, noise includes any interference or barriers that might compromise the understanding of the message, such as the distraction of the receiver, variations in the perceptions of receivers, or lack of appropriate knowledge or interest. The additional steps in an interactive communication model are: - Acknowledge. Upon receipt of a message, the receiver may signal (acknowledge) receipt of the message, but this does not necessarily mean agreement with or comprehension of the message—merely that it has been received. - Feedback/response. When the received message has been decoded and understood, the receiver encodes thoughts and ideas into a message and then transmits this message to the original sender. If the sender perceives that the feedback matches the original message, the communication has been successful. In communication between people, feedback can be achieved through active listening, described in Section 10.2.2.6. As part of the communication process, the sender is responsible for the transmission of the message, ensuring the information being communicated is clear and complete, and confirming the message is correctly interpreted. The receiver is responsible for ensuring that the information is received in its entirety, interpreted correctly, and acknowledged or responded to appropriately. These components take place in an environment where there will likely be noise and other barriers to effective communication.
8. Apa saja beda penggunaan Information management systems pada Manage Communications dan Monitor Communications?
PMIS pada Manage:
Described in Section 4.3.2.2. Project management information systems can ensure that stakeholders can easily retrieve the information they need in a timely way. Project information is managed and distributed using a variety of tools, including:
- Electronic project management tools. Project management software, meeting and virtual office support software, web interfaces, specialized project portals and dashboards, and collaborative work management tools.
- Electronic communications management. Email, fax, and voice mail; audio, video and web conferencing; and websites and web publishing.
- Social media management. Websites and web publishing; and blogs and applications, which offer the opportunity to engage with stakeholders and form online communities.
PMIS pada Monitor:
Described in Section 4.3.2.2. Project management information systems provides a set of standard tools for the project manager to capture, store, and distribute information to internal and external stakeholders with the information they need according the communications plan. The information contained in the system is monitored to assess its validity and effectiveness.
page.392
9. Bagaimana interpersonal dan team skills membantu Project Manager merencanakan komunikasi?
Interpersonal and team skills that can be used for this process include but are not limited to observation/conversation as described in Section 5.2.2.6. Discussion and dialogue with the project team helps determine the most appropriate way to update and communicate project performance, and to respond to requests from stakeholders for information. Observation and conversation enables the project manager to identify issues within the team, conflicts between people, or individual performance issues.
page.392
10. Apa saja beda maksud dan tujuan Plan Communications Management dengan Plan Stakeholder Engagement?
Plan Communications Management is the process of developing an appropriate approach and plan for project communication activities based on the information needs of each stakeholder or group, available organizational assets, and the needs of the project. The key benefit of this process is a documented approach to effectively and efficiently engage stakeholders by presenting relevant information in a timely manner.
11. Mengapa Communication Management Plan diperlukan saat melakukan Plan Stakeholder Engagement? Bagian apa sajakah yang diperlukan?
Karena Communication plan help to find the best way to communicate to stakeholder
page 584
12. Apa saja beda maksud dan tujuan Manage Communications dengan Manage Stakeholder Engagement?
Manage Communications is the process of ensuring timely and appropriate collection, creation, distribution, storage, retrieval, management, monitoring, and the ultimate disposition of project information.
page.
page. 379
Manage Stakeholder Engagement is the process of communicating and working with stakeholders to meet their needs and expectations, address issues, and foster appropriate stakeholder involvement.
page.523
13. Apa saja beda maksud dan tujuan Monitor Communications dengan Monitor Stakeholder Engagement?
Monitor Communications is the process of ensuring the information needs of the project and its stakeholders are met. page.388
Monitor Stakeholder Engagement is the process of monitoring project stakeholder relationships and tailoring strategies for engaging stakeholders through modification of engagement strategies and plans.
page. 530
14. Jelaskan bagaimana communication skills digunakan sebagai tools dan techniques dalam proses Manage Communications. Jelaskan teknik apa saja yang dapat digunakan?
Communication techniques that can be used for this process include but are not limited to: - Communication competence. A combination of tailored communication skills that considers factors such as clarity of purpose in key messages, effective relationships and information sharing, and leadership behaviors. - Feedback. Feedback is information about reactions to communications, a deliverable, or a situation. Feedback supports interactive communication between the project manager, team and all other project stakeholders. Examples include coaching, mentoring, and negotiating. - Nonverbal. Examples of nonverbal communication include appropriate body language to transmit meaning through gestures, tone of voice, and facial expressions. Mirroring and eye contact are also important techniques. The team members should be aware of how they are expressing themselves both through what they say and what they don’t say. - Presentations. A presentation is the formal delivery of information and/or documentation. Clear and effective presentations of project information to relevant stakeholders can include but are not limited to:
-- Progress reports and information updates to stakeholders
--Background information to support decision making;
--General information about the project and its objectives, for the purposes of raising the profile of the work of the project and the team; and --Specific information aimed at increasing understanding and support of the work and objectives of the project.
Presentations will be successful when the content and delivery take the following into account: --The audience, their expectations, and needs; and --The needs and objectives of the project and project team.
page.384
15. Sebutkan rumus dari potensial communication channels, bagaimana penggunaan rumus tersebut
N*(N-1)/2
While the 5th edition of the PMBOK defines a formula (which used to be asked in PMP exams as well), its 6th edition only mentions the number of potential communication channels, without setting out a formula. Therefore, the following subsection refers to the PMBOK 5th edition (ch, 10.1.2.1, p. 291-292).
The formula requires only one input parameter:
n = the number of stakeholders (or team members)
Formula to Calculate the Number of Communication Channels
The number of potential communication channels is calculated with the following formula:
Number of potential communication channels = n x (n-1)/2
In other words, the number of people involved is multiplied by itself after subtraction of 1 and subsequently divided by 2.
16. Apa saja isi EEF dan OPA yang diperlukan sebagai input di proses Manage Communications?
EEF Organizational culture, political climate, and governance framework Personnel administration policies Stakeholder risk thresholds Established communication channels, tools, and systems; Global, regional, or local trends and practices or habits Geographic distribution of facilities and resources OPA Corporate policies and procedures for social media, ethics, and security Corporate policies and procedures for issue, risk, change, and data management Organizational communication requirements Standardized guidelines for development, exchange, storage, and retrieval of information Historical information from previous projects, including the lessons learned repository
page 383
17. Bagaimana Stakeholder Engagement Matrix digunakan dalam proses Monitor Communications?
which can provide information about the effectiveness of the communications activities.
A data representation technique that can be used includes but is not limited to the stakeholder engagement assessment matrix (Section 13.2.2.5), which can provide information about the effectiveness of the communications activities. This is achieved by reviewing changes between desired and current engagement and adjusting communications as necessary.
page 392
18. Bagaimana perbedaan penggunaan interpersonal dan team skills di Plan Communication
Management, Manage Communications, dan Monitor Communications?
Plan Communication Management
Interpersonal and team skills that can be used for this process include but are not limited to: - Communication styles assessment. A technique used to assess communication styles and identify the preferred communication method, format, and content for planned communication activities. Often used with unsupportive stakeholders, this assessment may follow a stakeholder engagement assessment (described in Section 13.2.2.5) to identify gaps in stakeholder engagement that require additional tailored communication activities and artifacts. - Political awareness. Political awareness helps the project manager to plan communications based on the project environment as well as the organization’s political environment. Political awareness concerns the recognition of power relationships, both formal and informal, and also the willingness to operate within these structures. An understanding of the strategies of the organization, knowing who wields power and influence in this arena, and developing an ability to communicate with these stakeholders are all aspects of political awareness. - Cultural awareness. Cultural awareness is an understanding of the differences between individuals, groups, and organizations and adapting the project’s communication strategy in the context of these differences. This awareness and any consequent actions minimize misunderstandings and miscommunication that may result from cultural differences within the project’s stakeholder community. Cultural awareness and cultural sensitivity help the project manager to plan communications based on the cultural differences and requirements of stakeholders and team members.
page 375
Manage Communications
Interpersonal and team skills that can be used for this process include but are not limited to: - Active listening. Techniques of active listening involve acknowledging, clarifying and confirming, understanding, and removing barriers that adversely affect comprehension. - Conflict management. Described in Section 9.5.2.1. - Cultural awareness. Described in Section 10.1.2.6. - Meeting management. Meeting management is taking steps to ensure meetings meet their intended objectives effectively and efficiently. The following steps should be used for meeting planning: -- Prepare and distribute the agenda stating the objectives of the meeting. -- Ensure that the meetings start and finish at the published time. -- Ensure the appropriate participants are invited and attend. -- Stay on topic. -- Manage expectations, issues, and conflicts during the meeting. -- Record all actions and those who have been allocated the responsibility for completing the action. - Networking. Networking is interacting with others to exchange information and develop contacts. Networks provide project managers and their teams with access to informal organizations to solve problems, influence actions of their stakeholders, and increase stakeholder support for the work and outcomes of the project, thus improving performance. - Political awareness. Described in Section 10.1.2.6. Political awareness assists the project manager in engaging stakeholders appropriately to maintain their support throughout the project.
page.386
Monitor Communications
Interpersonal and team skills that can be used for this process include but are not limited to observation/conversation as described in Section 5.2.2.6. Discussion and dialogue with the project team helps determine the most appropriate way to update and communicate project performance, and to respond to requests from stakeholders for information. Observation and conversation enables the project manager to identify issues within the team, conflicts between people, or individual performance issues.
page 392
19.Jelaskan bagaimana komunikasi diperlukan untuk berhasilnya suatu project.
Communication is needed to communicate what is appropriate in project. Project Communications Management includes the processes necessary to ensure that the information needs of the project and its stakeholders are met through development of artifacts and implementation of activities designed to achieve effective information exchange. Project Communications Management consists of two parts. The first part is developing a strategy to ensure communication is effective for stakeholders. The second part is carrying out the activities necessary to implement the communication strategy.
page 359
20. Apa pengertian Stakeholder ?
An individual, group, or organization that may affect, be affected by, or perceive itself to be affected by a decision, activity, or outcome of a project, program, or portfolio.
page 723.
21. Apa isi dari stakeholder register?
Stakeholder Register. A project document including the identification, assessment, and classification of project stakeholders. The stakeholder register contains details about the identified stakeholders to help understand the knowledge they may have. page 101
22. Di proses groups apa saja stakeholder influence paling tinggi?
Planning
Executing
Monitor & Controlling
Page 556
23. Apakah Project Manager termasuk stakeholder?
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization that may affect, be affected by, or perceive itself to be affected
by a decision, activity, or outcome of a project. Project stakeholders may be internal or external to the project, they may
be actively involved, passively involved, or unaware of the project. Project stakeholders may have a positive or negative
impact on the project, or be positively or negatively impacted by the project. Examples of stakeholders include but are
not limited to:
- Internal stakeholders:
Project managers of other projects,
page 550
24. Apa itu Stakeholder Analysis? kenapa stakeholder butuh di analisa?
Stakeholder Analysis. A technique of systematically gathering and analyzing quantitative and qualitative information to determine whose interests should be taken into account throughout the project.
page 723
Stakeholder analysis. Stakeholder analysis results in a list of stakeholders and relevant information such as their positions in the organization, roles on the project, “stakes,” expectations, attitudes (their levels of support for the project), and their interest in information about the project. Stakeholders’ stakes can include but are not limited to a combination of: - Interest. A person or group can be affected by a decision related to the project or its outcomes. - Rights (legal or moral rights). Legal rights, such as occupational health and safety, may be defined in the legislation framework of a country. Moral rights may involve concepts of protection of historical sites or environmental sustainability. - Ownership. A person or group has a legal title to an asset or a property. - Knowledge. Specialist knowledge, which can benefit the project through more effective delivery of project objectives, organizational outcomes, or knowledge of the power structures of the organization. - Contribution. Provision of funds or other resources, including human resources, or providing support for the project in more intangible ways, such as advocacy in the form of promoting the objectives of the project or acting as a buffer between the project and the power structures of the organization and its politics.
page 512.
25. Sebutkan classification models yg digunakan untuk stakeholders analysis
Power/interest grid, power/influence grid, or impact/influence grid. Each of these techniques supports a grouping of stakeholders according to their level of authority (power), level of concern about the project’s outcomes (interest), ability to influence the outcomes of the project (influence), or ability to cause changes to the project’s planning or execution.
These classification models are useful for small projects or for projects with simple relationships between stakeholders and the project, or within the stakeholder community itself.
page 512
26. Nama lain authority adalah … sedang kan Nama lain influence adalah …
authority= power
influence=impact
page 512
27. Apakah saliance model itu? berdasarkan apa saja mendescribenya
Salience model. Describes classes of stakeholders based on assessments of their power (level of authority or ability to influence the outcomes of the project), urgency (need for immediate attention, either time-constrained or relating to the stakeholders’ high stake in the outcome), and legitimacy (their involvement is appropriate). There is an adaptation of the salience model that substitutes proximity for legitimacy (applying to the team and measuring their level of involvement with the work of the project). The salience model is useful for large complex communities of stakeholders or where there are complex networks of relationships within the community. It is also useful in determining the relative importance of the identified stakeholders.
page 513
28. Apa yg membedakan stakeholder yang harus di monitor, keep satisfied, manage closely dan keep informed? 29. Berikan contoh Stakeholder yg perlu di keep informed dan siapa yg perlu di keep satisfied
Directions of influence. Classifies stakeholders according to their influence on the work of the project or the
project team itself. Stakeholders can be classified in the following ways:
- Upward (senior management of the performing organization or customer organization, sponsor, and steering
committee), - Downward (the team or specialists contributing knowledge or skills in a temporary capacity), - Outward (stakeholder groups and their representatives outside the project team, such as suppliers, government departments, the public, end-users, and regulators), or - Sideward (the peers of the project manager, such as other project managers or middle managers who are in competition for scarce project resources or who collaborate with the project manager in sharing resources or information).
page.513
30. Sebutkan 5 engagement level dari stakeholder, sebutkan perbedaan2nya
The engagement level of stakeholders can be classified as follows: - Unaware. Unaware of the project and potential impacts. - Resistant. Aware of the project and potential impacts but resistant to any changes that may occur as a result of the work or outcomes of the project. These stakeholders will be unsupportive of the work or outcomes of the project. - Neutral. Aware of the project, but neither supportive nor unsupportive. - Supportive. Aware of the project and potential impacts and supportive of the work and its outcomes. - Leading. Aware of the project and potential impacts and actively engaged in ensuring that the project is a success.
page.521
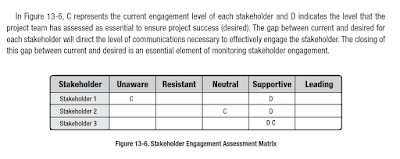
Mengapa pada Figure 13-7 Stakeholders Engagement Assessment Matrix, tidak ada D(Desired) di kolom Leading?
In Figure 13-6, C represents the current engagement level of each stakeholder and D indicates the level that the project team has assessed as essential to ensure project success (desired). The gap between current and desired for each stakeholder will direct the level of communications necessary to effectively engage the stakeholder. The closing of this gap between current and desired is an essential element of monitoring stakeholder engagement.
page 522
31. Apa maksud C (Current) dan D(Desired) di Figure 13-7?
C represents the current engagement level of each stakeholder and
D indicates the level that the project team has assessed as essential to ensure project success (desired).
page 522
32. Apa yg sama antara Stakeholder Management Plan dengan Communication Management Plan?
Plan Stakeholder Engagement. The process of developing approaches to involve project stakeholders, based on their needs, expectations, interests, and potential impact on the project. Plan Communications Management. The process of developing an appropriate approach and plan for project communication activities based on the information needs of each stakeholder or group, available organizational assets, and the needs of the project.
kedua nya berhubungan dengan stakeholder.
page 713
33. Apa beda Change request di Manage Stakeholder Engagement dan Monitor Stakeholder Engagement?
Manage Stakeholder Engagement
—The process of communicating and working with stakeholders to meet their needs and expectations, address issues, and foster appropriate stakeholder engagement involvement. Described in Section 4.3.3.4. As a result of managing stakeholder engagement, changes to the project scope or product scope may emerge. All change requests are processed for review and disposition through the Perform Integrated Change Control process (Section 4.6). Monitor Stakeholder Engagement
—The process of monitoring project stakeholder relationships and tailoring strategies for engaging stakeholders through the modification of engagement strategies and plans. Described in Section 4.3.3.4. A change request may include corrective and preventive actions to improve the current level of stakeholder engagement. Change requests are processed for review and disposition through the Perform Integrated Change Control process (Section 4.6). page 503, 529, 535
34. Sebutkan jenis2 Change Request di Manage Stakeholder Engagement dan Monitor Stakeholder Engagement?
CR di Manage Stakeholder Engagement: Changes to the project scope or product scope may emerge
35. Apa beda Issue log dan Change Log?
Issue Log. A project document where information about issues is recorded and monitored. Change Log. A comprehensive list of changes submitted during the project and their current status. page 700 , 709
36. Issue log menjadi input di proses mana saja?
Identify Stakeholder
Plan Stakeholder Engagement
Manage Stakeholder Engagement
Monitor Stakeholder Engagement
Manage Communication
Monitor Communication
page 381, 507
37. Apa beda Interpersonal Skills & Management Skills? Sebutkan contoh2nya
Interpersonal Skills. Skills used to establish and maintain relationships with other people.
Project managers accomplish work through the project team and other stakeholders. Project managers rely on important interpersonal skills, including, but not limited to: - Leadership, - Team building, - Motivating, - Communicating, - Influencing, - Decision making, - Political and cultural awareness, - Negotiating, - Facilitating, - Managing conflict, and - Coaching. Management Skills. The ability to plan, organize, direct, and control individuals or groups of people to achieve specific goals.
In addition to any specific technical skills and general management proficiencies required for the project, project
managers should have at least the following attributes:
- Knowledge about project management, the business environment, technical aspects, and other information
needed to manage the project effectively;
- Skills needed to effectively lead the project team, coordinate the work, collaborate with stakeholders, solve
problems, and make decisions;
- Abilities to develop and manage scope, schedules, budgets, resources, risks, plans, presentations, and
reports; and
- Other attributes required to successfully manage the project, such as personality, attitude, ethics, and leadership.
page 552, 709, 710


No comments:
Post a Comment